Beef Liver: A Nutritional Deep Dive for Weight Management
Thinking about adding beef liver to your weight loss journey? This comprehensive guide explores the potential benefits and risks of incorporating beef liver and its supplements into your diet. While not a magic bullet, beef liver's unique nutritional profile warrants careful consideration. We'll examine the science, explore safe usage, and offer practical advice to help you make informed decisions.
Nutritional Benefits of Beef Liver
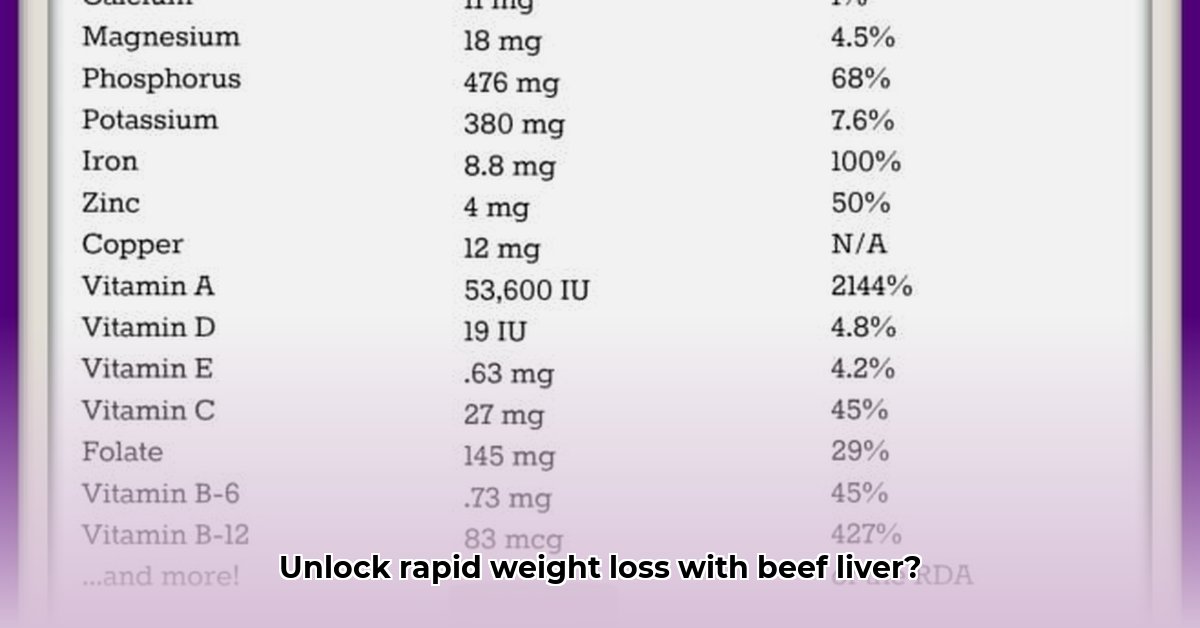
Beef liver is a nutritional powerhouse, exceptionally rich in vitamins and minerals crucial for metabolic function and overall well-being. It's a concentrated source of:
- Vitamin A: Essential for vision, immune function, and cell growth. However, excessive intake can be toxic.
- Vitamin B12: Crucial for nerve function, DNA synthesis, and red blood cell formation. Often deficient in vegetarians and vegans.
- Vitamin D: Supports bone health, immune function, and calcium absorption. Important for overall well-being.
- Iron: Essential for oxygen transport in the blood and energy production. Iron deficiency is a common nutritional deficiency.
- Copper: Plays a role in energy production, iron absorption, and connective tissue formation.
- Choline: Vital for brain health, liver function, and cell membrane structure. Often overlooked in discussions about nutrition.
- Selenium: A powerful antioxidant that protects cells from damage.
Multiple observational studies suggest a correlation between adequate intake of these nutrients and improved health markers, potentially impacting weight management indirectly through enhanced metabolism and energy levels. However, direct causal links between beef liver consumption and weight loss require further research. Does consuming beef liver directly aid in weight loss? The evidence remains inconclusive.
Potential Risks and Precautions
While beef liver offers significant nutritional benefits, several potential risks must be acknowledged:
- High Cholesterol: Beef liver is high in cholesterol, which can negatively affect cardiovascular health in susceptible individuals. This is particularly crucial for those with pre-existing conditions.
- High Vitamin A: The high concentration of Vitamin A presents a risk of toxicity if consumed in excess. Pregnant women and those with liver conditions should exercise extreme caution.
- High Purine Content: Beef liver is relatively high in purines, a potential concern for individuals with gout or hyperuricemia.
- Potential Contaminants: The risk of contamination from pesticides or other environmental toxins exists, especially with non-organic sources. Choosing organic, grass-fed beef liver minimizes this risk.
How can we mitigate the risks? Careful sourcing, moderate consumption, and awareness of personal health status are key.
Beef Liver Supplements: Benefits and Drawbacks
Beef liver supplements offer a concentrated source of nutrients, but they come with their own set of challenges:
Pros: Convenience and a potentially standardized nutrient profile (depending on the quality of the supplement).
Cons:
- Inconsistent Quality: Nutrient levels and purity can vary significantly between brands.
- Potential Contamination: The risk of contamination during manufacturing or sourcing remains.
- Cost: High-quality supplements can be expensive.
Always prioritize reputable brands with clear labeling, transparent sourcing, and third-party testing. Even with supplements, it is still advisable to consult your physician.
Incorporating Beef Liver into Your Diet: A Practical Guide
- Start Slowly: Begin with small portions (2-3 ounces) 2-3 times a week to assess tolerance and potential side effects.
- Choose Wisely: Opt for organic, grass-fed beef liver to minimize exposure to potential contaminants.
- Prepare Carefully: Experiment with various cooking methods (pan-frying, sautéing, stewing) to find what you enjoy and best retains nutrients.
- Listen to Your Body: Pay close attention to digestive responses and adjust consumption accordingly.
- Consult Your Doctor: Discuss incorporating beef liver into your diet, especially if you have pre-existing health conditions or are pregnant/breastfeeding.
- Supplement Cautiously: Only use supplements under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
Conclusion: A Balanced Perspective
While beef liver offers numerous nutritional benefits, its role in weight loss is not definitively established. It's crucial to consume it in moderation, prioritize quality sources, and be mindful of potential risks. Beef liver should be viewed as a potential supplement to a healthy lifestyle, not a primary weight-loss strategy. Always consult your healthcare provider before making significant dietary changes. Further research is needed to fully elucidate the relationship between beef liver consumption and weight management.